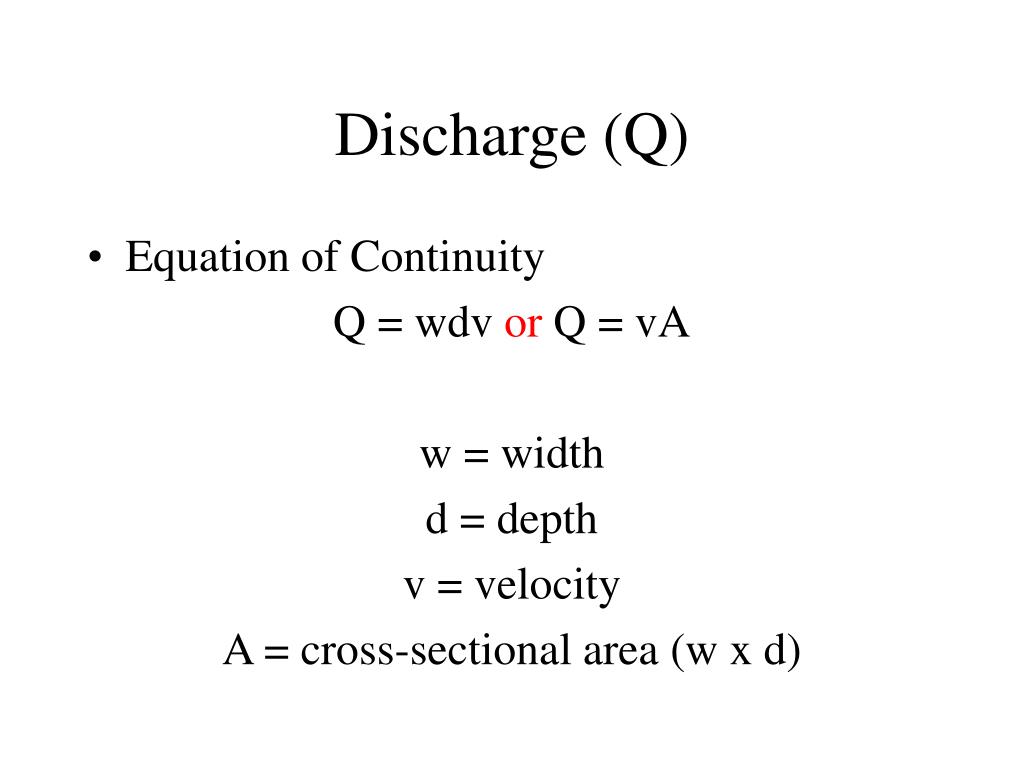
Discharge Formula - Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous. The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: \(q\) is the discharge rate in. \[ q = v \times a \] where:
\(q\) is the discharge rate in. The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: \[ q = v \times a \] where: Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous.
\(q\) is the discharge rate in. The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: \[ q = v \times a \] where: Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous.
Fluid Mechanics Chapter 4 Discharge and Mean Velocity YouTube
The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: \[ q = v \times a \] where: \(q\) is the discharge rate in. Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous.
Rate of discharge, discharge,, equation of continuity, continuity
Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous. \(q\) is the discharge rate in. \[ q = v \times a \] where: The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula:
PPT CROSS REGULATOR PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2160973
\[ q = v \times a \] where: The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous. \(q\) is the discharge rate in.
Calculate the discharge coefficient using equations
The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous. \(q\) is the discharge rate in. \[ q = v \times a \] where:
Derive discharge equation for rectangular notch. Fluid Mechanics YouTube
\[ q = v \times a \] where: \(q\) is the discharge rate in. The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous.
Cippolletti Notch/Weir Fluid Mechanics Derivation of discharge
Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous. The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: \[ q = v \times a \] where: \(q\) is the discharge rate in.
Discharge and Continuity equation YouTube
The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous. \[ q = v \times a \] where: \(q\) is the discharge rate in.
[Solved] solve the following 9] Compute the discharge over a
Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous. \[ q = v \times a \] where: The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: \(q\) is the discharge rate in.
Discharge and How to Calculate Discharge YouTube
\[ q = v \times a \] where: The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: \(q\) is the discharge rate in. Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous.
PPT Fluvial Hydraulics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
\[ q = v \times a \] where: \(q\) is the discharge rate in. The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: Learn the definitions and formulas of discharge or flow rate, and the types of flow such as laminar, turbulent, steady, uniform and continuous.
Learn The Definitions And Formulas Of Discharge Or Flow Rate, And The Types Of Flow Such As Laminar, Turbulent, Steady, Uniform And Continuous.
The discharge rate is calculated using a simple formula: \[ q = v \times a \] where: \(q\) is the discharge rate in.