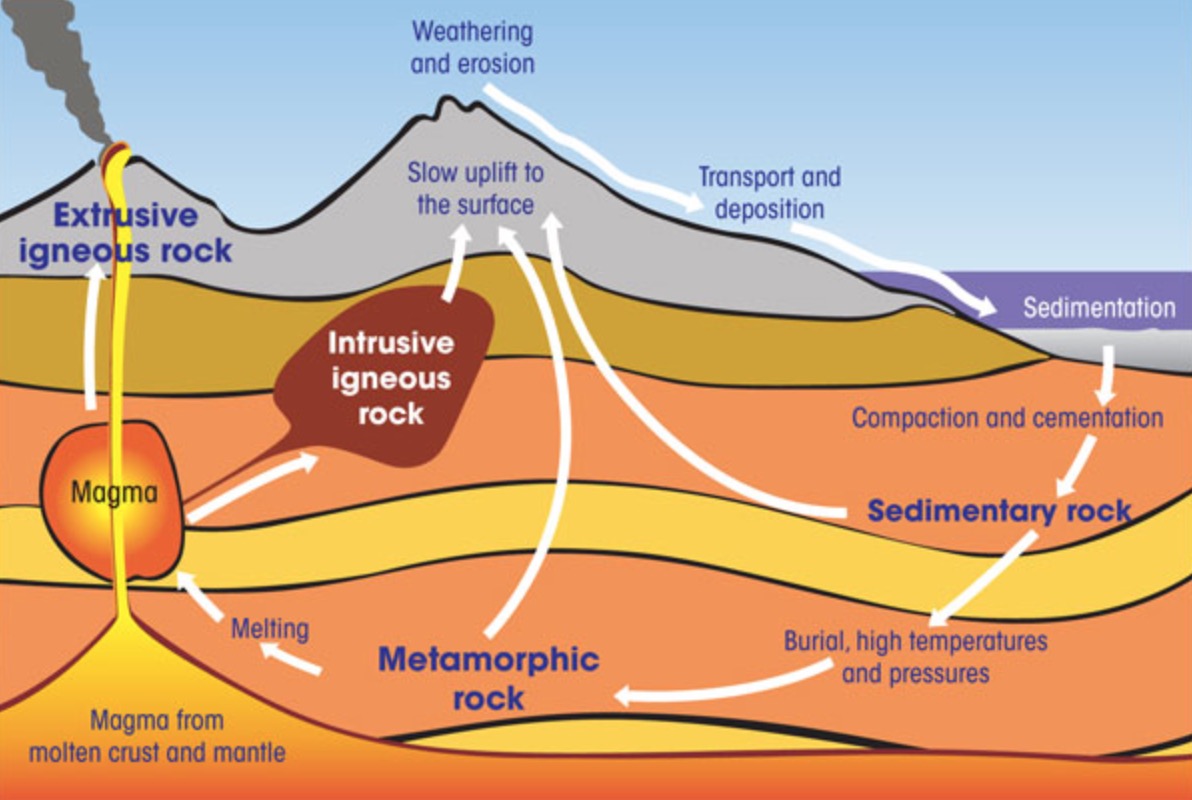
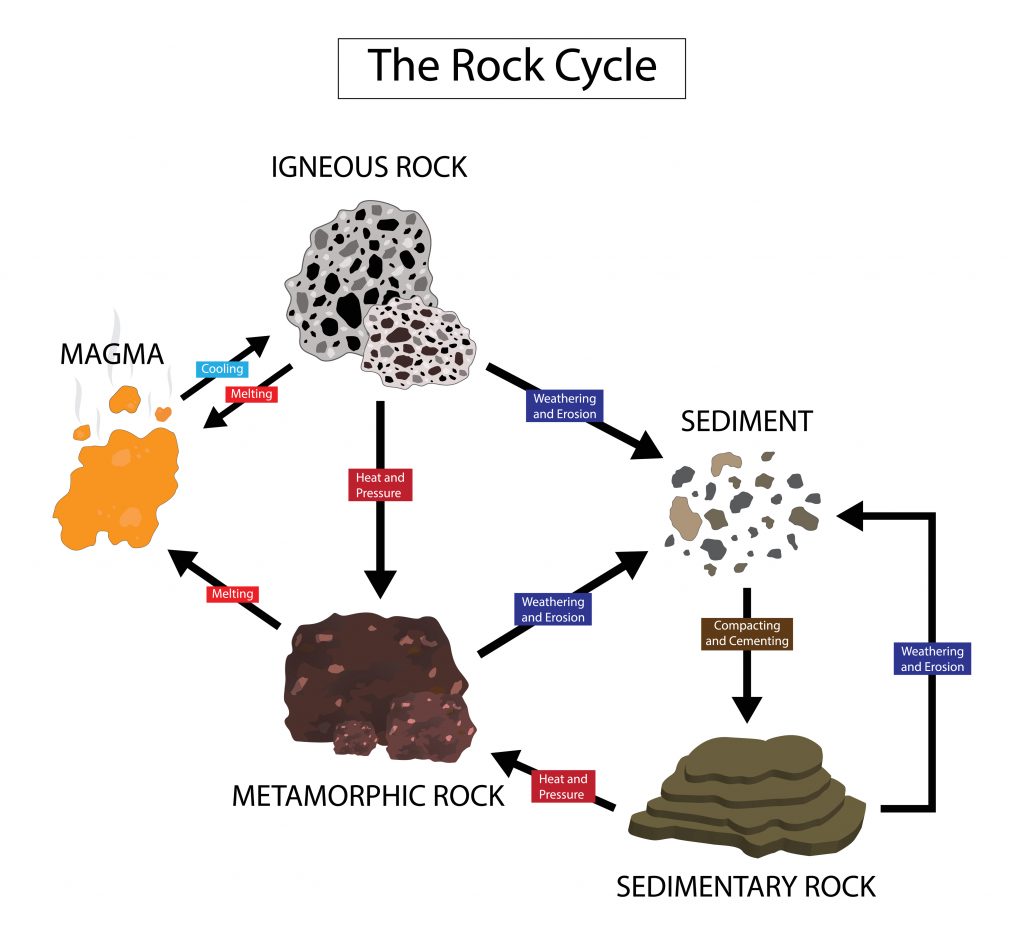
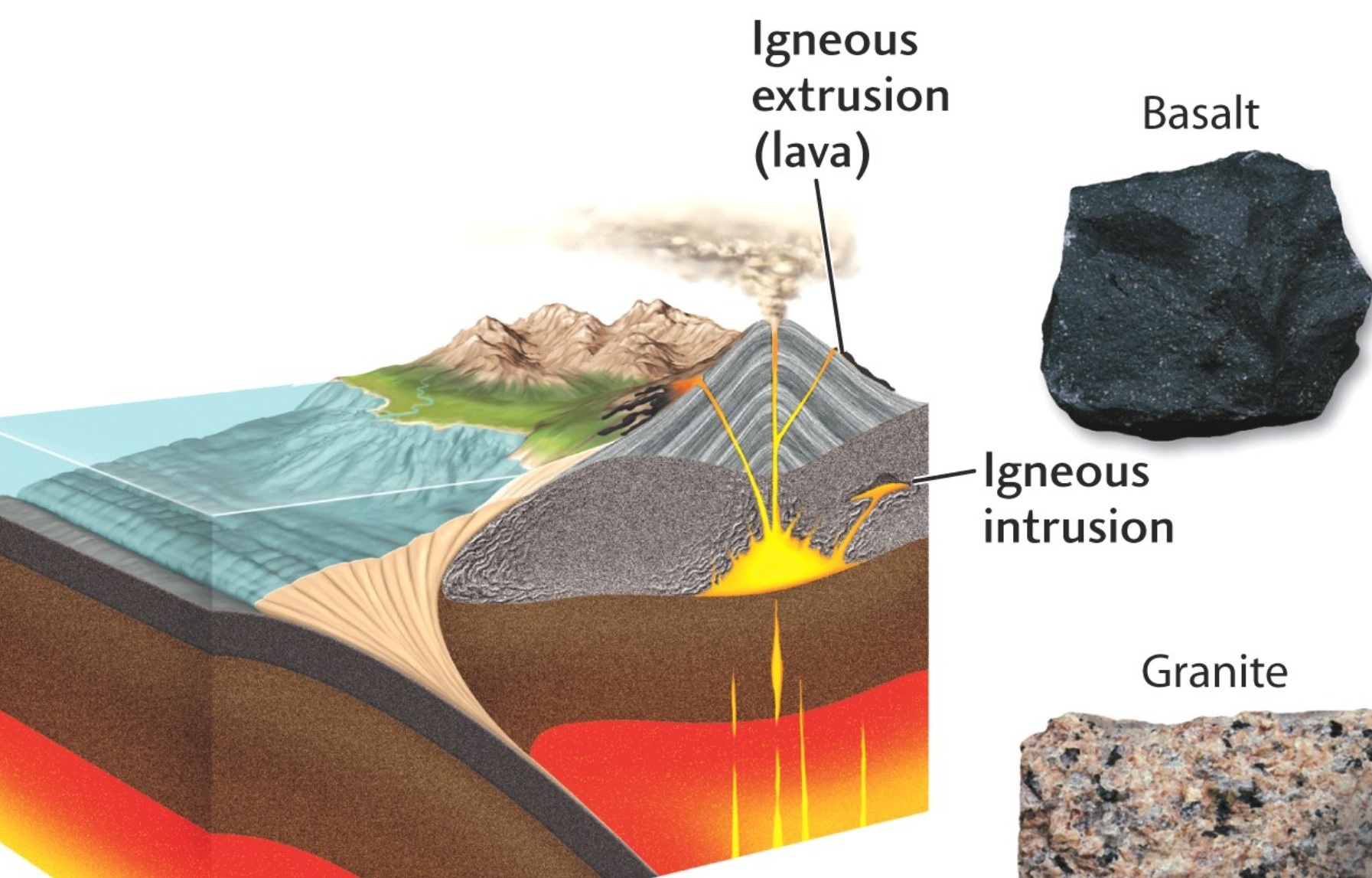
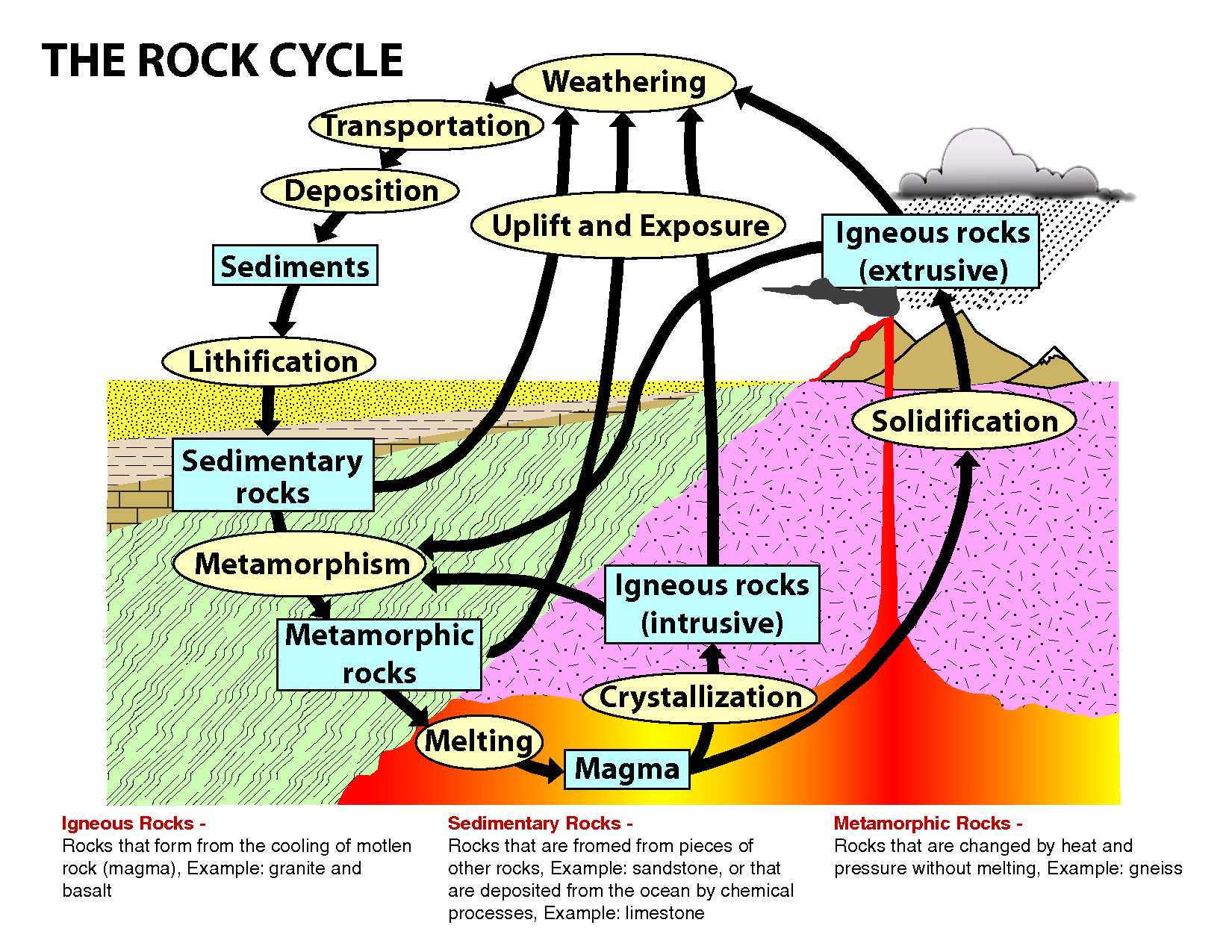
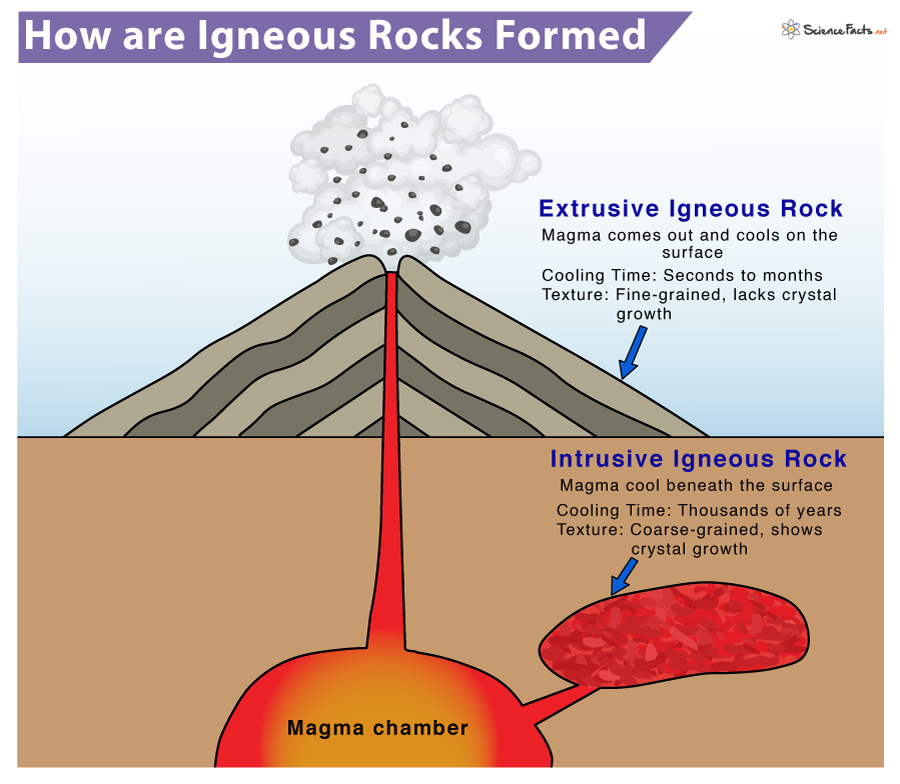
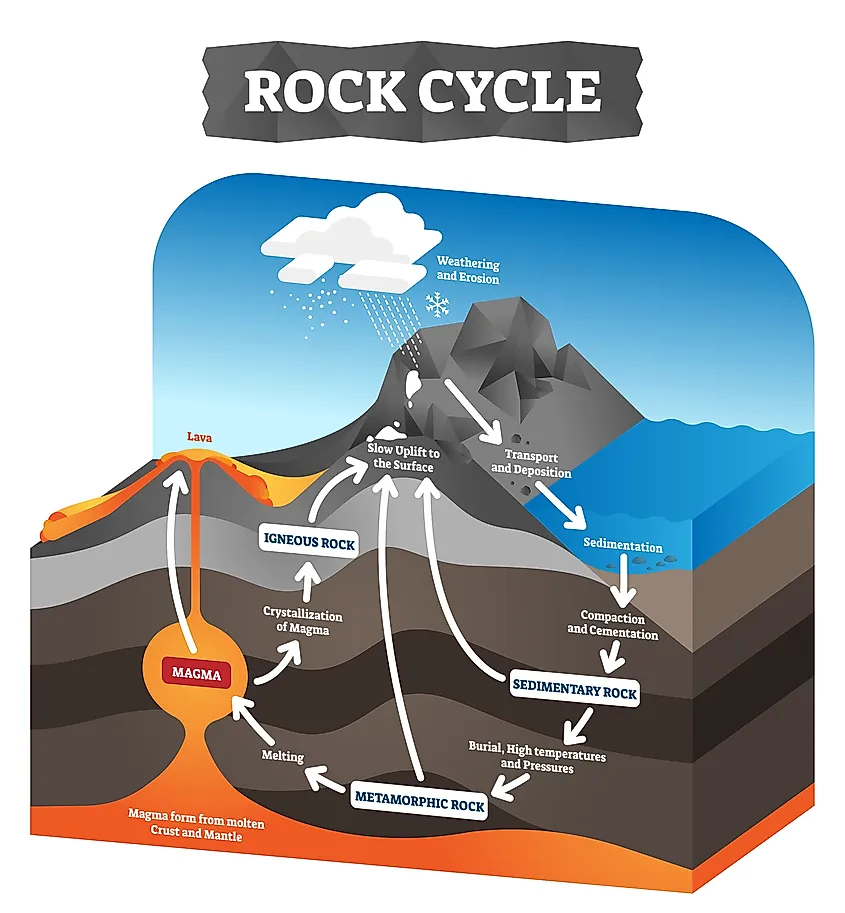
Igneous Rock Formation Diagram - Since their constituent minerals are. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Though they vary widely in. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material.
Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Since their constituent minerals are. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Though they vary widely in. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and.
Since their constituent minerals are. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Though they vary widely in. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and.
Top 7 Differences Between Metamorphic Rocks and Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Since their constituent minerals are. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Though they.
A Beginner's Guide to Types of Rock Igneous, Sedimentary, and
These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Since their constituent minerals are. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Though they vary widely in. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially.
Igneous/Sedimentry/Metamorphic Rocks Maya's Blog
Since their constituent minerals are. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Though they.
Igneous Rocks Definition, Classification and Examples Geology News
Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Though they vary widely in. Since their.
Fun Igneous Rocks Facts for Kids
Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Though they vary widely in. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Since their.
lesson 4 Igneous rock formation YouTube
Since their constituent minerals are. Though they vary widely in. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic.
Geology Fundamentals Identifying Igneous Rocks in the Field Geology
These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Though they vary widely in. Since their constituent minerals are. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic.
Rocks Geography study Material & Notes
Though they vary widely in. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Since their constituent minerals are. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. These include olivine, pyroxene,.
Igneous Rocks Definition, Types, Examples, & Pictures
Though they vary widely in. Since their constituent minerals are. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks. Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. These include olivine, pyroxene,.
How Are Igneous Rocks Formed? WorldAtlas
Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Though they vary widely in. Since their constituent minerals are. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic.
Since Their Constituent Minerals Are.
Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of magma, which is a hot (600 to 1,300 °c, or 1,100 to 2,400 °f) molten or partially molten rock material. Though they vary widely in. These include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, and. Igneous rocks comprise one of the three principal classes of rocks, the others being metamorphic and sedimentary rocks.