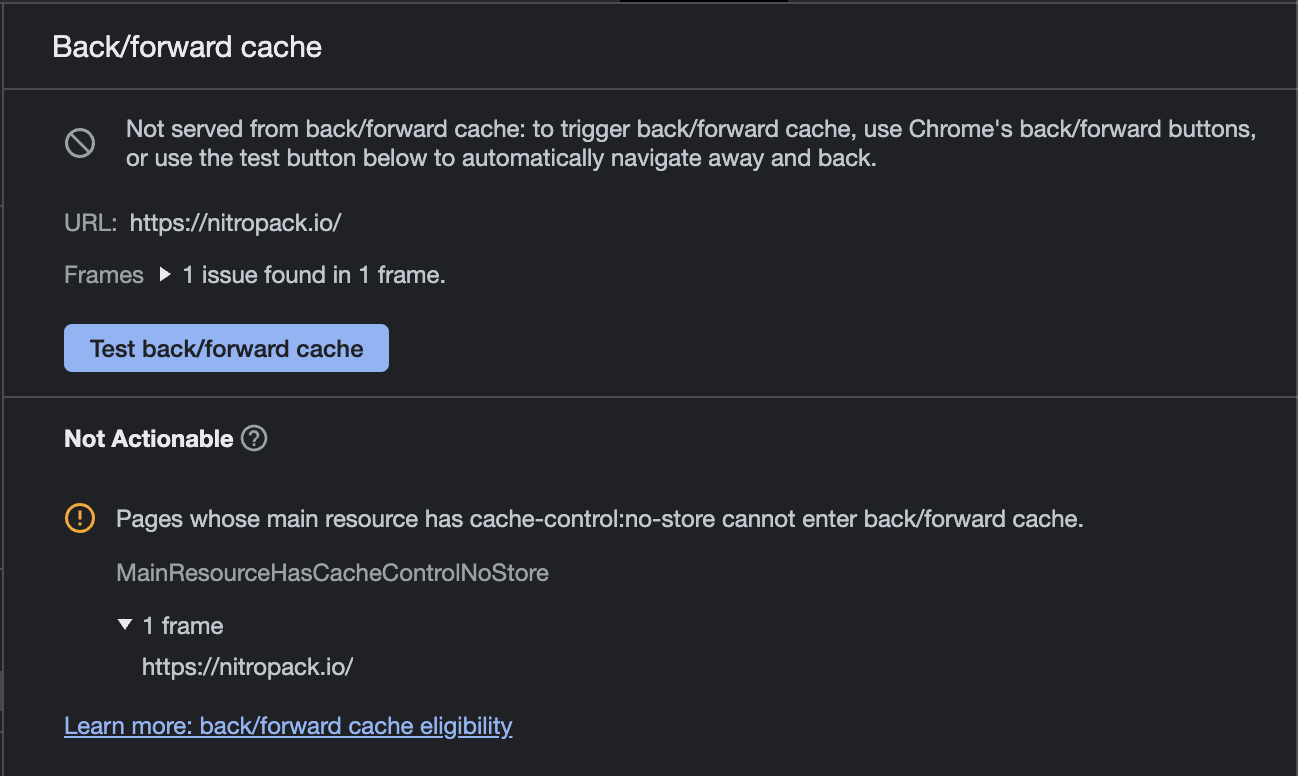
Page Prevented Back Forward Cache Restoration - Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up.
If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up.
If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again.
Back/Forward Cache What It Is and How to Use It to Serve Content
The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again.
Lighthouse scanning performance issue Page prevented back/forward
If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again. The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and.
bfcache Improve Back & Forward Page Views Aaron T. Grogg
If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up.
What Does The Back/Forward Cache Mean For Site Speed? DebugBear
The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again. If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and.
What Different Navigation Types Mean For Page Speed DebugBear
With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again.
Back/Forward Cache What It Is and How to Use It to Serve Content
The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again.
Back/Forward Cache What It Is and How to Use It to Serve Content
The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again.
Back/Forward Cache What It Is and How to Use It to Serve Content
If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again.
Test back/forward cache Chrome DevTools Chrome for Developers
If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again.
The Day Jimmy Page Prevented the Electricity Board From Erecting Pylons
Many navigations are performed by going back to a previous page, or forwards again. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating. The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up.
Many Navigations Are Performed By Going Back To A Previous Page, Or Forwards Again.
The back/forward cache (bfcache) can speed up. With back/forward cache (bfcache), instead of destroying a page when the user navigates away, we postpone destruction and. If a page supports the back/forward cache (also called bfcache), the browser saves the full page state in memory when navigating.