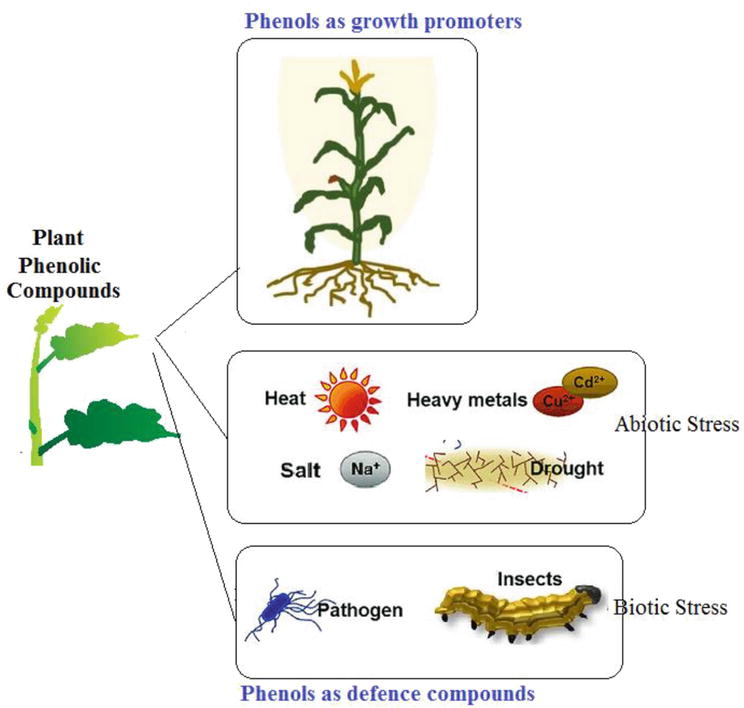
Phenols In Plants - Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological. Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as.
Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as.
Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et.
Plant phenolic compounds
Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites.
Basic structure of (A). Some of the simplest phenols and flavonoids
Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate.
Defence Mechanism in Plants PDF Phenols Plants
Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Phenols function as allelochemicals for.
Classification of plant phenols. Here, phenols of plant origin are
Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological. Phenols function as allelochemicals for.
Metabolic pathway and chemical structure of plant phenolics
Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites.
Phenolic Compounds, Phenolic Compounds in Plants
Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites.
Phenolic Compounds in the Plant Development and Defense An Overview
Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological. Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate.
Biosynthesis of phenols and flavonoids. According to Song et al
Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological. Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate.
Examples of phenolic compounds. Download Scientific Diagram
Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Phenols function as allelochemicals for.
Phenol, 1089502, तरल फिनोल in Lower Parel, Mumbai , SOLVAY
Plant phenolics are generally involved in defense against ultraviolet radiation or aggression by pathogens, parasites and predators, as well as. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites.
Plant Phenolics Are Generally Involved In Defense Against Ultraviolet Radiation Or Aggression By Pathogens, Parasites And Predators, As Well As.
Phenols function as allelochemicals for competing plants and weeds and as phytoestrogens for mammals. Biosynthesis of phenol compounds in the pentose phosphate, shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways in plants (modified from vattem et. Phenolic compounds are the most abundant secondary metabolites in plants, showing a wide range of distinct biological.