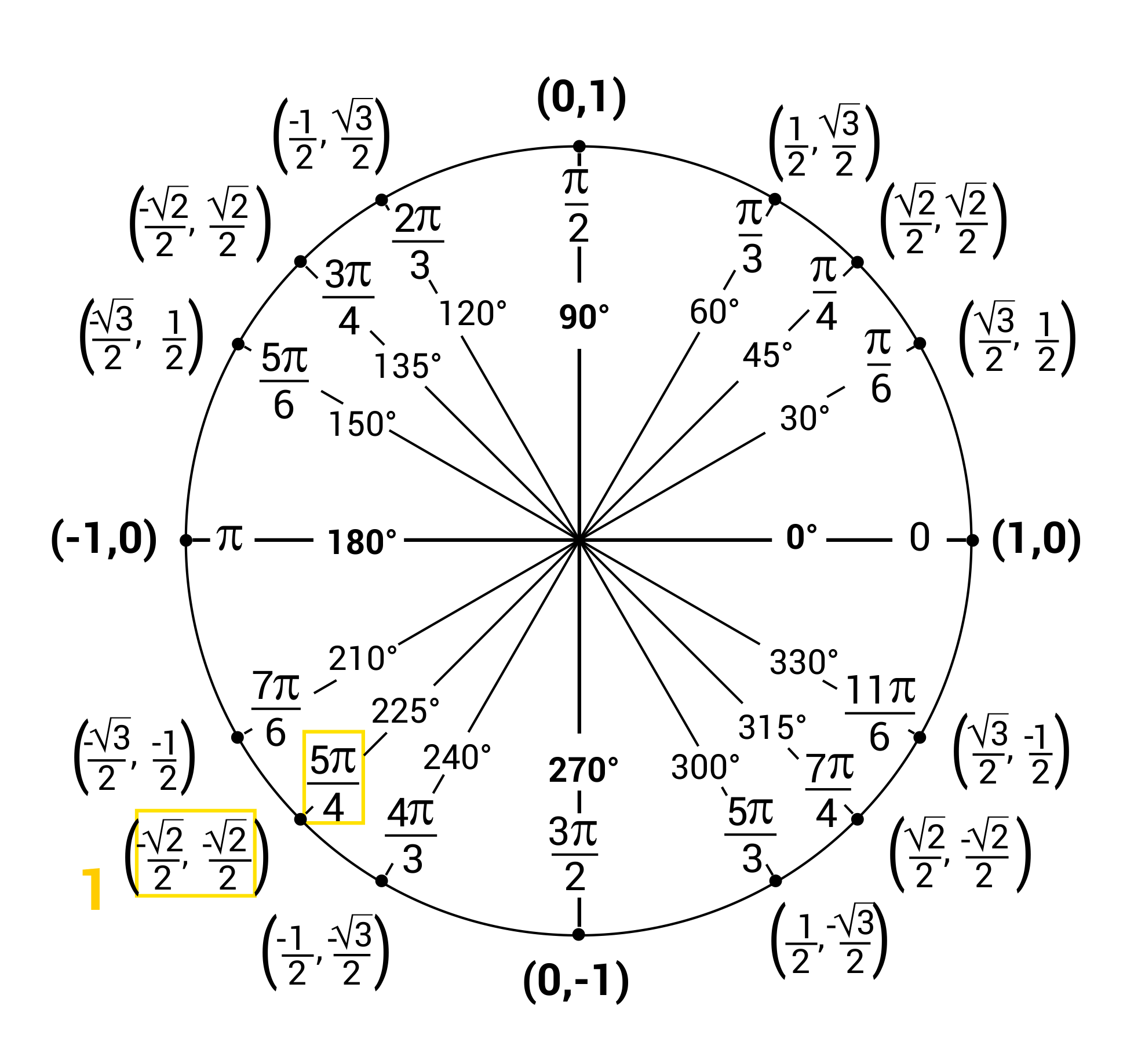
What Is The Reference Angle For 5Pi 3 - The reference angle of 3π/4 will be π/3. The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine & tangent are negative), and its reference angle is 60 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The angle is, ⇒ 5π / 3. Here, we can clearly see that. To find the reference angle for 5π/3, we need to determine the equivalent angle within one full. Therefore the correct option is b. Since 5π/3 radians is more than π (180°), it is located in the fourth quadrant of the unit. Given, angle in radians = 5π/3. The reference angle for 5π/3 is π/3. The latter is known as the vertex of the angle and the rays as the sides, sometimes as the legs and sometimes the arms of the angle.
The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine & tangent are negative), and its reference angle is 60 degrees with respect to the horizontal. Here, we can clearly see that. The reference angle for 5π/3 is π/3. Given, angle in radians = 5π/3. The reference angle of 3π/4 will be π/3. The latter is known as the vertex of the angle and the rays as the sides, sometimes as the legs and sometimes the arms of the angle. To find the reference angle for 5π/3, we need to determine the equivalent angle within one full. The angle is, ⇒ 5π / 3. Since 5π/3 radians is more than π (180°), it is located in the fourth quadrant of the unit. Therefore the correct option is b.
The latter is known as the vertex of the angle and the rays as the sides, sometimes as the legs and sometimes the arms of the angle. Since 5π/3 radians is more than π (180°), it is located in the fourth quadrant of the unit. The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine & tangent are negative), and its reference angle is 60 degrees with respect to the horizontal. Here, we can clearly see that. To find the reference angle for 5π/3, we need to determine the equivalent angle within one full. Therefore the correct option is b. The angle is, ⇒ 5π / 3. Given, angle in radians = 5π/3. The reference angle of 3π/4 will be π/3. The reference angle for 5π/3 is π/3.
pi/3 is the reference angle for A. 2pi/3 B. 15pi/3 C. 7pi/3 D. 19pi/3
The angle is, ⇒ 5π / 3. The reference angle of 3π/4 will be π/3. The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine & tangent are negative), and its reference angle is 60 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The latter is known as the vertex of the angle and the rays as the.
What is the reference angle and cosine of StartFraction 7 pi Over 6
Given, angle in radians = 5π/3. The latter is known as the vertex of the angle and the rays as the sides, sometimes as the legs and sometimes the arms of the angle. Therefore the correct option is b. The reference angle for 5π/3 is π/3. The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine.
Reference Angles NBKomputer
Therefore the correct option is b. The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine & tangent are negative), and its reference angle is 60 degrees with respect to the horizontal. Since 5π/3 radians is more than π (180°), it is located in the fourth quadrant of the unit. The angle is, ⇒ 5π /.
Unit Circle Practice Worksheets
To find the reference angle for 5π/3, we need to determine the equivalent angle within one full. The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine & tangent are negative), and its reference angle is 60 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The reference angle of 3π/4 will be π/3. The angle is, ⇒ 5π.
The reference angle for (5pi)/4 is pi/4 , which has a terminal point of
Given, angle in radians = 5π/3. The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine & tangent are negative), and its reference angle is 60 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The reference angle of 3π/4 will be π/3. Since 5π/3 radians is more than π (180°), it is located in the fourth quadrant of.
Ex Sine And Cosine Values Using The Unit Circle Multiples, 54 OFF
The reference angle for 5π/3 is π/3. Therefore the correct option is b. The angle is, ⇒ 5π / 3. Here, we can clearly see that. Since 5π/3 radians is more than π (180°), it is located in the fourth quadrant of the unit.
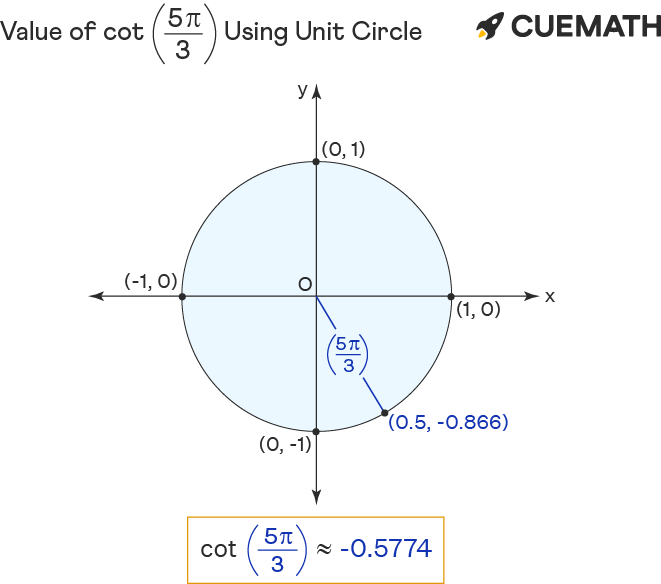
Cot 5pi/3 Find Value of Cot 5pi/3 Cot 5π/3
The reference angle for 5π/3 is π/3. Here, we can clearly see that. Therefore the correct option is b. The latter is known as the vertex of the angle and the rays as the sides, sometimes as the legs and sometimes the arms of the angle. The angle is, ⇒ 5π / 3.
Angle Of Rotation Examples
The latter is known as the vertex of the angle and the rays as the sides, sometimes as the legs and sometimes the arms of the angle. To find the reference angle for 5π/3, we need to determine the equivalent angle within one full. Since 5π/3 radians is more than π (180°), it is located in the fourth quadrant of.
for this special angle, draw the angle and find the reference angle t
To find the reference angle for 5π/3, we need to determine the equivalent angle within one full. The reference angle of 3π/4 will be π/3. Therefore the correct option is b. Since 5π/3 radians is more than π (180°), it is located in the fourth quadrant of the unit. The angle is, ⇒ 5π / 3.
inverse trigonometric functions and reference angles for the following
The angle is, ⇒ 5π / 3. The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine & tangent are negative), and its reference angle is 60 degrees with respect to the horizontal. To find the reference angle for 5π/3, we need to determine the equivalent angle within one full. Therefore the correct option is b..
The Latter Is Known As The Vertex Of The Angle And The Rays As The Sides, Sometimes As The Legs And Sometimes The Arms Of The Angle.
To find the reference angle for 5π/3, we need to determine the equivalent angle within one full. Given, angle in radians = 5π/3. Therefore the correct option is b. Since 5π/3 radians is more than π (180°), it is located in the fourth quadrant of the unit.
The Reference Angle Of 3Π/4 Will Be Π/3.
The reference angle for 5π/3 is π/3. The angle is, ⇒ 5π / 3. The angle 5pi/3 is in the fourth quadrant (meaning cosine is positive while sine & tangent are negative), and its reference angle is 60 degrees with respect to the horizontal. Here, we can clearly see that.