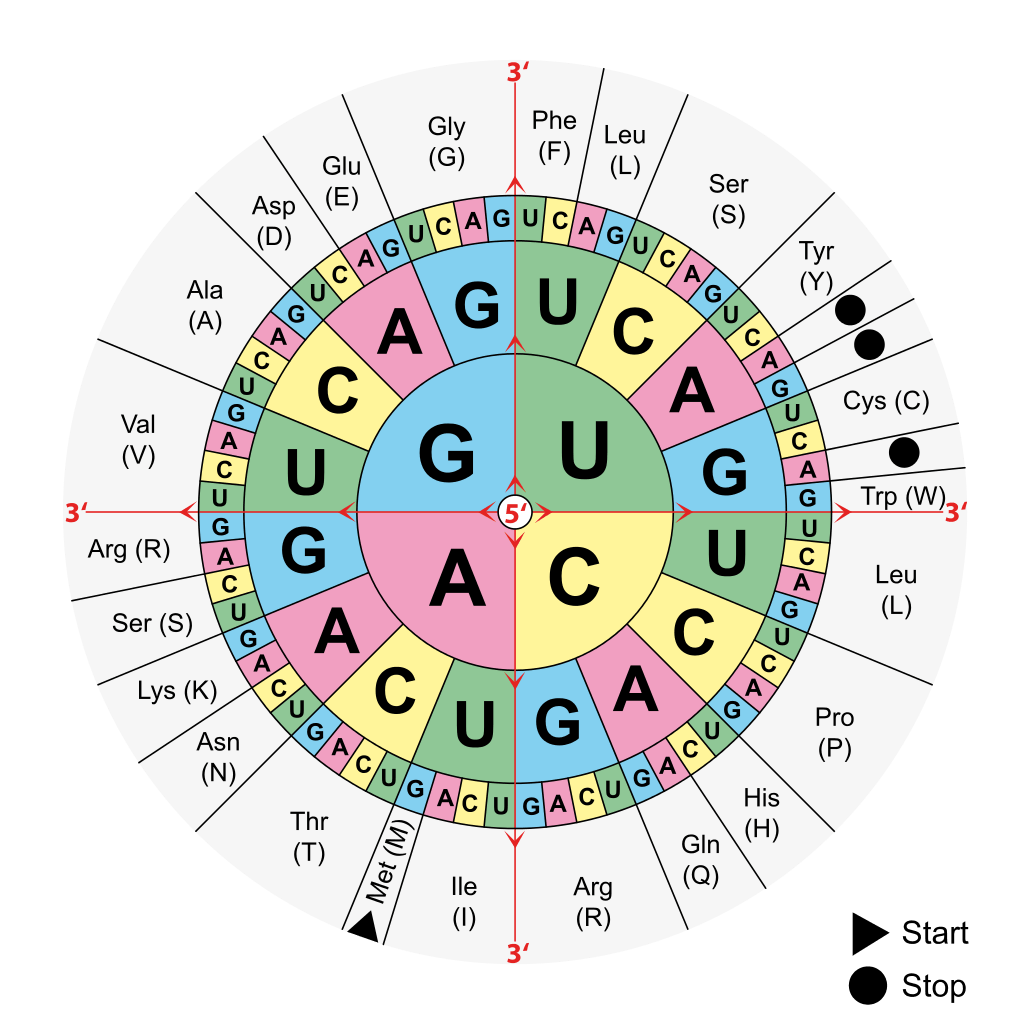
What Recognizes Stop Codons - Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: The termination factors are necessary to recognize stop codons (uag, uga, and uaa) and to release the complete protein chain from the elongation trna. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation. However, in bacteria, a pair of class 1 rfs, namely rf1 and. Figure 2 shows the 64 codon combinations and the amino. In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons.
Figure 2 shows the 64 codon combinations and the amino. In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons. However, in bacteria, a pair of class 1 rfs, namely rf1 and. The termination factors are necessary to recognize stop codons (uag, uga, and uaa) and to release the complete protein chain from the elongation trna. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons:
However, in bacteria, a pair of class 1 rfs, namely rf1 and. Figure 2 shows the 64 codon combinations and the amino. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons. The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation. The termination factors are necessary to recognize stop codons (uag, uga, and uaa) and to release the complete protein chain from the elongation trna.
What Is Stop Codon? Science Trends
In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons. The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation. Figure 2 shows the 64 codon combinations and the amino. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: The termination factors are.
(PDF) Diverse bacterial genomes encode an operon of two genes, one of
The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: However, in bacteria, a pair of class 1 rfs, namely rf1 and. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved.
(PDF) [Translation termination factor of eRFI of the ciliate
The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons. However, in bacteria, a pair of class 1 rfs, namely rf1 and. The termination.
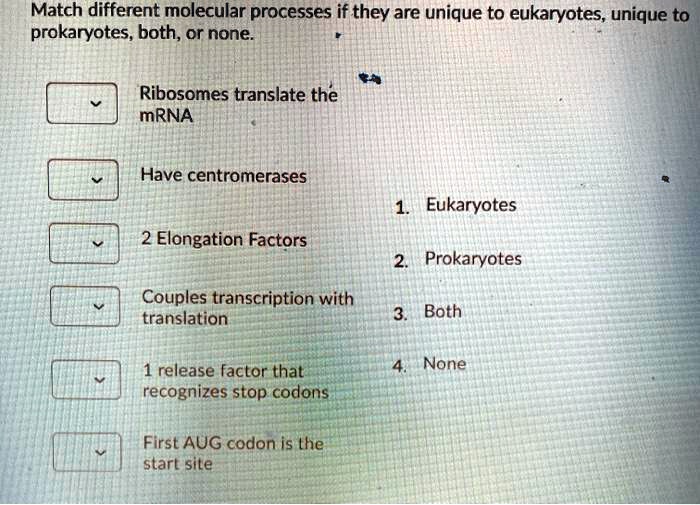
SOLVEDMatch different molecular processes if they are unique to
Figure 2 shows the 64 codon combinations and the amino. The termination factors are necessary to recognize stop codons (uag, uga, and uaa) and to release the complete protein chain from the elongation trna. In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three.
Solved wa URDI 68. What recognizes the stop codons in an
However, in bacteria, a pair of class 1 rfs, namely rf1 and. The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: The termination factors are necessary to recognize stop codons (uag, uga, and uaa) and to.
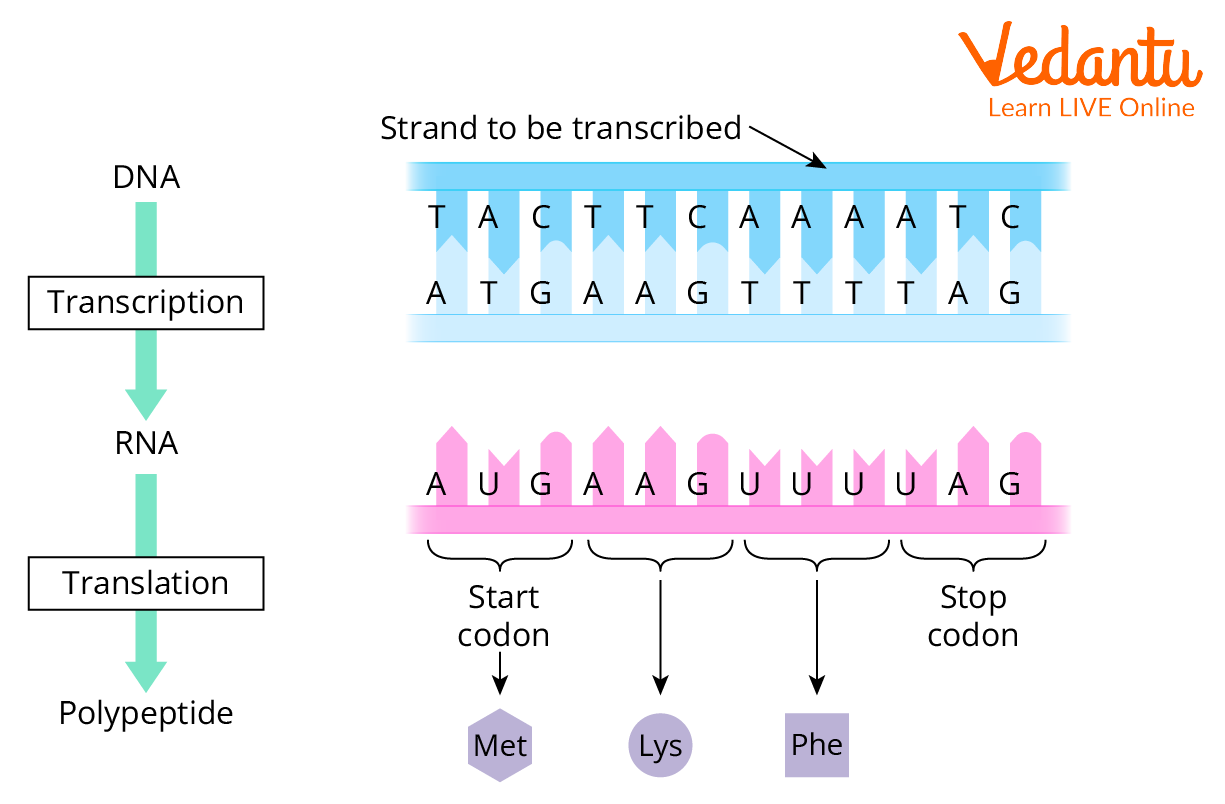
Start Codons in DNA and RNA Definition, Important Questions, and FAQs
In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons. The termination factors are necessary to recognize stop codons (uag, uga, and uaa) and to release the complete protein chain from the elongation trna. The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation. However, in bacteria, a pair of class.
Stop Codons and Protein Synthesis Identifying the Recognizing Agents
Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: The termination factors are necessary to recognize stop codons (uag, uga, and uaa) and to release the complete protein chain from the elongation trna. Figure 2 shows the 64 codon combinations and the amino. In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes.
Termination of Translation Chris Avins Elizabeth Durante Christine
In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons. Figure 2 shows the 64 codon combinations and the amino. The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the termination of translation. However, in bacteria, a pair of class 1 rfs, namely rf1 and. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome.
SOLVED Which of the following events occur during eukaryotic
Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons. The codons uaa, uag, and uga are the stop codons that signal the.
Pensoft Writing Tool
However, in bacteria, a pair of class 1 rfs, namely rf1 and. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons: The termination factors are necessary to recognize stop codons (uag, uga, and uaa) and to release the complete protein chain from the elongation trna. Figure 2 shows the 64 codon combinations.
The Codons Uaa, Uag, And Uga Are The Stop Codons That Signal The Termination Of Translation.
The termination factors are necessary to recognize stop codons (uag, uga, and uaa) and to release the complete protein chain from the elongation trna. Figure 2 shows the 64 codon combinations and the amino. In eukaryotes, a single class 1 rf, erf1, recognizes all three stop codons. Termination of protein synthesis occurs when a translating ribosome encounters one of three universally conserved stop codons:
Termination Of Protein Synthesis Occurs When A Translating Ribosome Encounters One Of Three Universally Conserved Stop Codons:
However, in bacteria, a pair of class 1 rfs, namely rf1 and.